Getty Images
Getty Images
Letter from Africa: Ethiopia’s lost Armenian community
In our series of letters from African journalists, Ismail Einashe takes a trip to Ethiopia to find out about a lost community.
My search for the last Armenians of Ethiopia began in Piassa, the bustling commercial centre of the old part of the capital, Addis Ababa.
On previous visits to the city, I had always been intrigued by the snippets I had heard about the community and its history.
There had long been a connection between Ethiopia and Armenia through the Orthodox Church. But this developed beyond priests, to bring in diplomats and traders.
In the 19th Century, a handful of Armenians played a vital role in the court of Emperor Menelik II.
And later, in the early 20th Century, a community settled that went on to have an economic and cultural impact in the country.
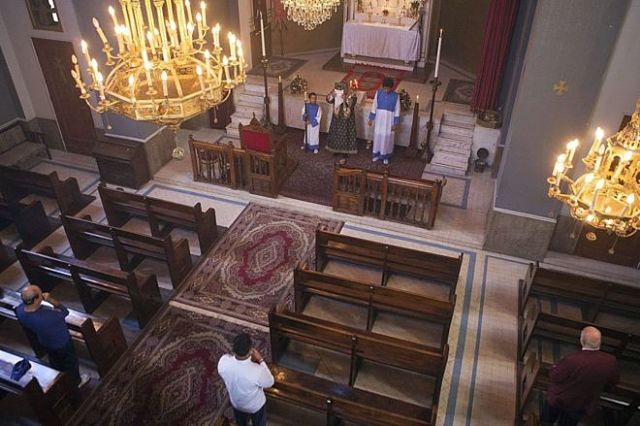
On a sticky afternoon, I stood outside the gates of the exquisite St George Armenian Apostolic Holy Church that was built in the 1930s.
It looked closed but I called out “selam” – “hello” in Amharic.
A confused-looking elderly security guard came out and after I explained that I wanted to look around, he went to fetch Simon, the Armenian-Ethiopian caretaker.
The quiet, dignified man came out and told me that they do not get many visitors.
Haile Selassie’s influence
The church is rarely open, as there is no priest these days, and the community, of no more than 100, is mostly elderly.
Inside the church, the altar is ornately decorated and red Persian rugs cover the floor.
This was the heart of the community that began to grow in numbers during the rule of Haile Selassie who, as Ras Tafari, became prince regent of Ethiopia in 1916 and Emperor from 1930 to 1974.
Under his leadership, Ethiopia began to rapidly modernise and Armenian courtiers, businessmen and traders played an important role in this transition.
In 1924, Ras Tafari visited the Armenian monastery in Jerusalem, where he met a group of 40 children who had been orphaned by the mass killing of Armenians by Ottoman Turks during World War One.
Moved by their plight, he asked the Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem if he could take them to Ethiopia and look after them there.
The 40 orphans, or arba lijoch in Amharic, were all trained in music and went on to form the imperial brass band of Ethiopia.
Despite their small numbers the Armenian community had a crucial role in ushering Ethiopia into the modern world”
They were led by an Armenian, Kevork Nalbandian, who composed the imperial anthem.
The community reached its zenith in the 1960s when it numbered 1,200.
Despite their small numbers they had a crucial role in ushering Ethiopia into the modern world – from helping to develop the distinctive Ethiopian jazz style to working as tailors, doctors, business people and serving in the imperial court.
—
Join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.