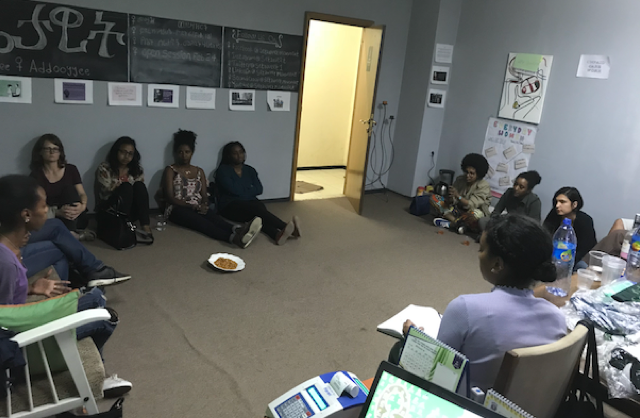
Although a language around women's rights is largely absent from national discussions, Ethiopia's capital, Addis Ababa, is home to a burgeoning women's movement. The city is witnessing growing activity including the first openly declared feminist group called Setaweet. (Photo: Setaweet gathering in Addis by Hasabie Kidanu).
Although a language around women's rights is largely absent from national discussions, Ethiopia's capital, Addis Ababa, is home to a burgeoning women's movement. The city is witnessing growing activity including the first openly declared feminist group called Setaweet. (Photo: Setaweet gathering in Addis by Hasabie Kidanu).
Tadias Magazine
By Hasabie Kidanu

Published: July 24th, 2018
Addis Ababa (TADIAS) – As one of the world’s oldest continuous nation states Ethiopia upkeeps and exports a particular image to the rest of the world — a never-colonized, cradle of life that remains superior to European dominance. The culture is ancient and native with its indigenous national language, music and dress traditions considered sacrosanct. Ethiopia grows at its own pace, and looks inward.
In 2018, Ethiopia has one of the fastest growing national economies in the world and is nested in global networks of wealth, yet the perceived influence of foreign ideas are regarded warily. In a guarded and proud culture social change at the national scale is slow and painstaking. And in spite of generations of evolving global discourses focused on women’s rights, the subordinate position still held by women remains largely undiscussed.
Within this cultural context, how do we make language for an Ethiopian women’s movement? What do we call it? What have we called it in the past? And how do we define, grow, and adapt it? A younger generation of women has grown unsatisfied with the culture’s precedent for male hegemony in both public and domestic spheres. How do we redefine the role of women with liberation, leadership and sisterhood in mind? The greatest challenge facing an Ethiopian women’s movement today is how to fashion a homegrown language, which catalyzes change. How do we elevate consciousness within culture so committed to its customs, traditions and social structures that tends to place women on its margins?
From political participation and property ownership to healthcare access and education the social and legal lag of gender equality is evident here. Most acts of daily violence and domestic abuse go legally unchecked and garner little public outcry. Openly sharing one’s story of gender-based violence remains a taboo. Only a very slim portion of cases of sexual assault in the home and/or workplace are reported and even fewer cases make it to the courts. Media continues to perpetuate and dictate stale ideologies of the Ethiopian woman’s image, responsibility, and behavior. The daily catcall is as common as ever, and can easily escalate to physical violence. How do we raise a generation of women and men who no longer internalize and normalize sexism and violence?
Although a language around women’s rights is largely absent from national discussions, Ethiopia’s capital, Addis Ababa, is home to a burgeoning women’s movement. The city is witnessing growing activity including the first openly declared feminist group called Setaweet. Setaweet (the Amharic term for ‘of woman’) is the brainchild of Dr. Sehin Teferra, and it started essentially as a meeting, which later morphed into ‘The Setaweet Circle.’ It was, and still is, a safe space for Addis Ababa women to convene. Gathering together from all walks of life women involved with Setaweet speak candidly about their experiences in the workplace, home, city. From these gatherings the ‘Setaweet Open Sessions’ were born, and a free forum open to the public was developed to invite guest speakers, authors, and historians to tackle subjects concerning women’s issues. Here, everything is laid bare — even topics of Ethiopian culture that elsewhere are off limits. Topics such as the all-male clergy of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church, patrilineal family structures, as well as male privilege and entitlement are discussed. In addition, the Setaweet PLC provides a variety of services and custom designed trainings for public schools, corporate offices, and agencies on women’s leadership, sexual harassment, and gender-based violence.
Setaweet has organized various campaigns throughout the city, often with the support of their partner groups such as the Ethiopian Women’s Lawyers Association (EWLA), and The Yellow Movement — a group founded by Addis Ababa University law program faculty and students. Some of the projects include #AcidAttackEducationCampaign (2017); #PagumeActivism initiated by the Yellow Movement to create a platform for sharing incidences of everyday sexism on social media; #AriffAbbat (2017), a collaboration between the Embassy of Sweden and Setaweet to host a photo contest to celebrate and encourage engaged fatherhood; and #NothingforGranted (2018), a collaboration with the European Union Delegation to celebrate the contributions of Ethiopian women through photography.
However, it’s not so much ‘Setaweet,’ but the term ‘feminism’ that has become the trigger word. One of the greatest obstacles and complications of this particular word is that it signals a western import and a foreigner’s ethics onto Ethiopia. It pulls with it a connotation that it has ‘arrived’ to contaminate local customs and religious practices, and the ever-so-cherished Ethiopiawee Bahil. Even though the country has integrated many Western ideals in the past — from clothing, to architecture, to films, music, and food — feminism has not received an easy welcome. Surely, feminism is not new. Although Setaweet is the first to openly identify as a ‘feminist’ collective there have been organized women’s groups that have inched the needle forward for women’s health, legal reforms, social and economic participation.
Ethiopia has not generally witnessed waves of feminism (as we have seen in the West) or properly recorded or historicized organized women’s movements, however, Setaweet has had to sustain criticism that it is ‘too western, radical, hip’ or that the need to champion women as a culture pales in comparison to more nation-pressing issues of prosperity, security, and peace.
“Our goal is clear, it’s activism. The cultural specificity of a city like Addis Ababa is not lost on us,” says co-founder Sehin. “We have declared ourselves feminists. Perhaps other organizations who work to champion women’s rights may not use the word due to the stigma that is associated with the word here. We understand the banner of feminism originally responds to the challenges faced by women in the English speaking world. Yet, work needs to be done here, so fighting for gender equality at home means finding language specific to the challenges facing women in Ethiopia, and how we can raise consciousness to confront Ethiopia’s most closely held cultural ideals. Part of that includes teasing out when and where the Amharic language and media imaging are giving way to harmful and/or sexist attitudes towards the Ethiopian woman.”
Setaweet moves forward still growing and expanding its breadth. The role and need for it is undeniable. In four short years its following has increased while the responsibilities have broadened tremendously. Setaweet has become somewhat of a hotline for the city and community to share, unload, and call out injustices from all over the country – from sexist advertisements in pop-culture to cases of gender-based violence in universities and households. Anything and everything concerning women’s issues is circled through their main channels on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Perhaps, Setaweet’s most fundamental goal and achievement is that it is fostering an environment for conversation, and in return creating a space for language to evolve within the culture’s context.
—
You can learn more about Setaweet on Facebook at https://www.facebook.com/pg/SetaweetMovement.
Join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.