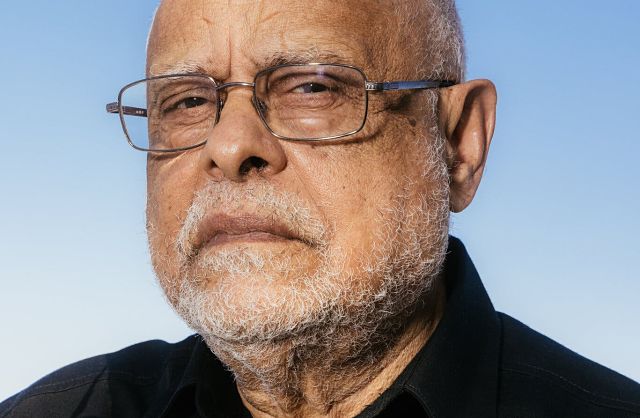
The Ethiopian American filmmaker Haile Gerima said he had “no trust in, no desire to be a part of” Hollywood. The director, an eminence of American and African indie cinema, is being recognized by the Academy Museum of Motion Pictures and Netflix. But he has long rejected the industry. (NYT)
The Ethiopian American filmmaker Haile Gerima said he had “no trust in, no desire to be a part of” Hollywood. The director, an eminence of American and African indie cinema, is being recognized by the Academy Museum of Motion Pictures and Netflix. But he has long rejected the industry. (NYT)
The New York Times
Haile Gerima doesn’t hold back when it comes to his thoughts on Hollywood. The power games of movie producers and distributors are “anti-cinema,” he put it recently. The three-act structure is akin to “fascism” — it “numbs, makes stories toothless.” And Hollywood cinema is like the “hydrogen bomb.”
For decades, Gerima, the 75-year-old Ethiopian filmmaker, has blazed a trail outside of the Hollywood system, building a legacy that looms large over American and African independent cinema.
But as he spoke with me on a video call from his studio in Washington, D.C., Gerima found himself at an unexpected juncture: He was about to travel to Los Angeles, where he would receive the inaugural Vantage Award at the opening gala of the Academy Museum of Motion Pictures, which is also screening a retrospective of his work this month. A new 4K restoration of his 1993 classic, “Sankofa,” debuted on Netflix last month.
After 50 years, Hollywood has finally come calling. “I’m going with a lump in my throat,” Gerima said with his typical candor. “This is an industry I have no relationship with, no trust in, no desire to be a part of.”
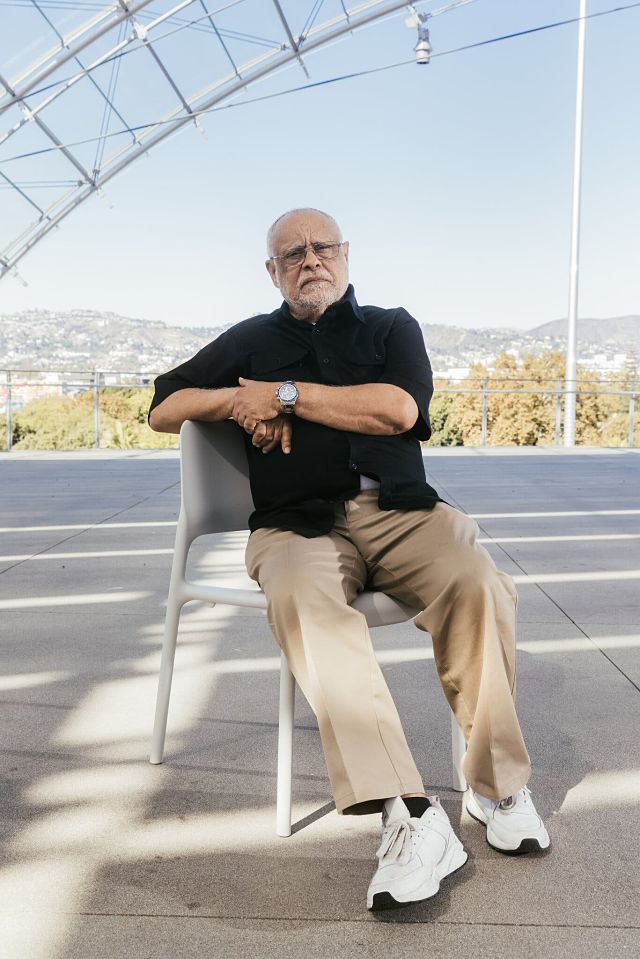

Gerima’s ideas about self-distribution influenced Ava DuVernay and other filmmakers. (Photo: The New York Times)
Gerima tends to speak directly and without euphemism, his words propelled by the force of his conviction. The filmmaker has been at loggerheads with the American film industry since the 1970s, when he was a student at the University of California, Los Angeles. There, he was part of what came to be known as the L.A. Rebellion — a loose collective of African and African American filmmakers, including Charles Burnett (“Killer of Sheep”), Julie Dash (“Daughters of the Dust”), Larry Clark (“Tamu”) and others, who challenged the mainstream cinematic idiom.
Gerima’s first project in film school was a short commercial called “Death of Tarzan.” An exorcism of Hollywood’s colonial fantasies, it provoked a response from a classmate that Gerima still remembers fondly: “Thank you, Gerima, for killing that diaper-wearing imperialist!”
The eight features he has since directed bristle with the same impulse for liberation, employing nonlinear narratives and jagged audiovisual experiments to paint rousing portraits of Black and Pan-African resistance. In a phone interview, Burnett described Gerima’s work as coursing with emotion: “People have plots and things, but he has energy, real energy. That’s what characterizes his films.”
The stark, black-and-white “Bush Mama” (1975) charts the radicalization of a woman in Los Angeles as she navigates poverty and the Kafkaesque bureaucracy of welfare. “Ashes and Embers” (1982) — which opens with the protagonist driving into Los Angeles with dreams of Hollywood before being abruptly stopped by the police — traces the gradual disillusionment of a Black Vietnam War veteran. In “Sankofa,” one of Gerima’s most acclaimed films, an African American model is transported back in time to a plantation, where she’s caught up in a slave rebellion. Other films, like “Harvest: 3,000 Years” (1976) and “Teza” (2008), explore the political history of Gerima’s native Ethiopia.
For the filmmaker and his wife and producing partner, Shirikiana Aina, these visions of fierce Black independence are as much a matter of life as art. Most of Gerima’s movies have been produced and distributed by the couple’s company, Mypheduh Films, which derives its name from an ancient Ethiopian word meaning “protector of culture.” Mypheduh’s offices are housed in Sankofa, a bookstore and Pan-African cultural center across the street from Howard University, where Gerima taught filmmaking for over 40 years. This little pocket of Washington is Gerima’s empire — or his “liberated territory,” as he likes to call it.
“When I think of Haile’s cinema, I think of the cinema of the maroon,” Aboubakar Sanogo, a friend of Gerima’s and a scholar of African cinema at Carleton University in Ottawa, Canada, said in an interview, invoking a term for runaway slaves who formed their own independent settlements. “It’s very much a cinema of freedom. Hollywood is the plantation from which he has escaped.”
If Gerima is now ready to dance with the academy (which, incidentally, has never awarded a best director Oscar to a Black filmmaker), it’s because of the involvement of a kindred soul: Ava DuVernay.
The “Selma” filmmaker, who co-chaired the Academy Museum’s opening gala, has been the driving force behind the Haile-ssance of 2021. Array, DuVernay’s distribution and advocacy collective, spearheaded the restoration of “Sankofa.” The company also rereleased “Ashes and Embers” on Netflix in 2016, in addition to distributing “Residue,” the debut feature by Gerima’s son Merawi, last year.
Speaking by phone, DuVernay said that in collaborating with Gerima, she felt she had come full circle: Years ago, she modeled Array on the example set by Gerima and Aina’s grass-roots distribution initiatives.
Read the full article at nytimes.com »
—
Join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.