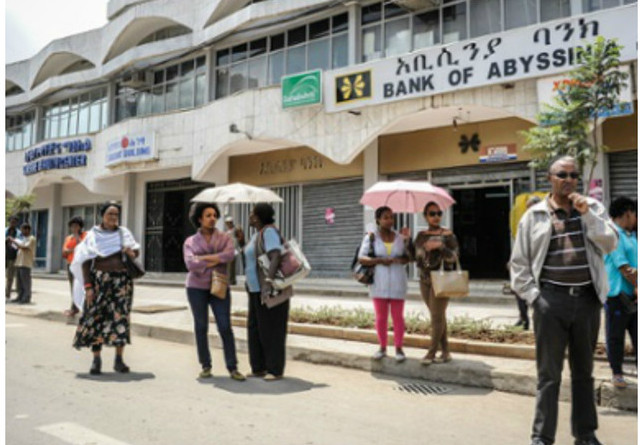
People wait for a bus in Addis Ababa. The government has launched an ambitious modernisation plan in the Ethiopian capital. (Photograph: Giorgio Cosulich/Getty)
People wait for a bus in Addis Ababa. The government has launched an ambitious modernisation plan in the Ethiopian capital. (Photograph: Giorgio Cosulich/Getty)
It is now three decades since Ethiopia experienced the infamous famine that cost the lives of more than a million people. The tragedy prompted the BBC’s Michael Buerk to describe it as “a biblical famine in the 20th century” and “the closest thing to hell on Earth”.
In sharp contrast with that devastating poverty, Ethiopia is now widely considered to be one of a pack of “African tigers”, with ambitious plans to become a middle-income country by 2025. The nation has, “like the proverbial phoenix, managed to rise from the ashes to become Africa’s fastest-growing non-energy-driven economy”, a senior tax adviser at KPMG Kenya recently noted.
The changes that have taken place in Ethiopia since the 1984 famine are commendable. Despite some dispute over the figures, there is consensus that Ethiopia has registered impressive economic growth for the past decade of somewhere between 8% and 10%. One effect of the progress is a greater capacity to cope with drought, preventing the descent into famine conditions that have occurred in the past. Ethiopia’s development efforts are also praised internationally for meeting some of the millennium development goals, particularly universal primary education and a reduction in infant mortality.
Read more at The Guardian »
—
Related:
Ethiopia, 30 Years After the 1984 Famine (The Guardian)
Ethiopian famine: how landmark BBC report influenced modern coverage (The Guardian)
Ethiopia: The famine report that shocked the world (BBC)
Join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.